CFMS
CFMS stands for Comprehensive Financial Management System.It’s an online system designed to streamline and manage an organization’s financial activities.There are various CFMS implementations,but they generally share some core functionalities.in this blog post we will explain what cfms is,Services offered,features,Status check and Login process etc.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Post | CFMS |
| Possible Full Names | Comprehensive Financial Management System, Corporate Financial Management System |
| Area | Government Finance |
| Purpose | Automate and streamline financial processes within a government organization |
| Typical Users | -Government agencies (e.g., departments, ministries) – Financial managers – Budget analysts – Vendors – Citizens (for some functions) |
| Benefits | -Increased transparency and accountability – Improved efficiency and accuracy – Faster processing of payments and invoices – Enhanced budgeting and forecasting capabilities – Reduced risk of fraud and errors |
| Key Functions | -Budgeting and planning – Accounts payable and receivable management – Cash flow management – Reporting and analytics – Procurement and contract management (may vary by system) |
| Typical Features | -Secure web-based platform – Role-based access control – Workflow automation – Integration with other government systems – Reporting tools and dashboards |
| Official website | https://cfms.ap.gov.in/ |
Contents
services offered by CFMS
The services offered by CFMS depend on the specific implementation, but here’s a breakdown of the two main categories:
Government Sector CFMS:
• Government to Government (G2G): This facilitates interactions and transactions between different government entities. For example, streamlining fund transfers between departments.
• Government to Employee (G2E): Provides services and resources specifically for government employees. This might include online paystubs, expense claim processing, or pension information access.
• Government to Citizen (G2C): Offers various services directly to citizens. This could include tracking bill payments, scholarship applications, or tax filing.
• Government to Business (G2B): Supports businesses with necessary government-related services and transactions. Examples include vendor registration, submitting invoices electronically, or tracking tax payments.
Private Sector “CFMS” (often referred to as ERP):
While not always called CFMS, many private companies utilize Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems that offer similar functionalities.These services can include:
• Financial Accounting: Recording financial transactions, managing accounts payable and receivable, payroll processing, and maintaining general ledgers.
• Budgeting and Forecasting: Creating and managing budgets, allocating funds, tracking expenses, and generating financial forecasts.
• Cash Flow Management: Forecasting receipts and payments, optimizing bank balances, and managing short-term investments.
• Reporting and Analysis: Generating reports on financial performance, identifying trends, and providing insights for decision-making.
Additional Considerations:
• Some CFMS implementations may offer additional functionalities specific to the organization’s needs.
• The level of access to different services within a CFMS will vary depending on the user’s role (citizen, employee, department head, etc.).
Core Functionalities of a CFMS
• Budgeting and Planning: CFMS allows for creating and managing budgets, allocating funds, and tracking expenses against those allocations.
• Accounting: The system facilitates recording financial transactions, including accounts payable and receivable, payroll, and general ledger.
• Cash Management: CFMS helps manage cash flow, including forecasting receipts and payments, and optimizing bank balances.
• Reporting and Analysis: The system generates reports that provide insights into financial performance, identify trends, and support decision-making.
• Regulatory Compliance: CFMS can help ensure adherence to relevant financial regulations and reporting requirements.
Benefits of Implementing a CFMS
• Improved Efficiency: Automating financial processes saves time and reduces manual errors.
• Enhanced Transparency: Real-time access to financial data improves transparency and accountability.
• Better Decision-Making: Data-driven insights from reports support better financial decisions.
• Increased Collaboration: CFMS facilitates collaboration across departments involved in financial activities.
• Reduced Costs: This online portal has increased efficiency and reduced cost.
Considering a CFMS
Organizations considering a CFMS implementation should:
• Identify Needs: Clearly define the specific financial management challenges they aim to address.
• Evaluate Options: Research different CFMS solutions and compare features to find the best fit.
• User Adoption: Ensure user-friendly interfaces and provide adequate training for smooth implementation.
• Data Security: Prioritize robust data security measures to protect sensitive financial information.
CFMS Login
The steps to log in to a CFMS depend on the specific system you’re dealing with.

Government Sector CFMS (e.g., Andhra Pradesh CFMS):
1.Identify the Relevant Portal: Different states or government departments in India might have their own CFMS portals. Search online for the specific CFMS you need.
2.Locate the Login Section: Most CFMS portals will have a prominent “Login” button on the homepage.
3.Enter Credentials: You’ll likely need to enter your User ID and Password.These credentials might be provided by your employer, government department, or created during a prior registration process.
4.Select Language (Optional): Some CFMS allow you to choose your preferred language for the interface.
5.Click “Login”: Once you’ve entered your credentials and chosen your language (if applicable), click the login button to access the system.
Private Sector “CFMS” (ERP Systems):
1.Access the Internal System: You’ll likely need to log in to a company-specific internal system. This might involve accessing a web portal or using a dedicated software application.
2.Enter Login Credentials: You’ll need to enter your employee ID and password assigned by your company’s IT department.
3.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) (Optional): Some companies might require additional authentication steps like entering a one-time password (OTP) received via SMS or authenticating through a mobile app.
4.Access the CFMS Module: Once logged in to the internal system, you might need to locate the specific module related to financial management.This could be labeled “ERP,” “Finance,” or something similar.
CFMS Status Check
The steps to check CFMS status depend on the specific CFMS implementation you’re dealing with.
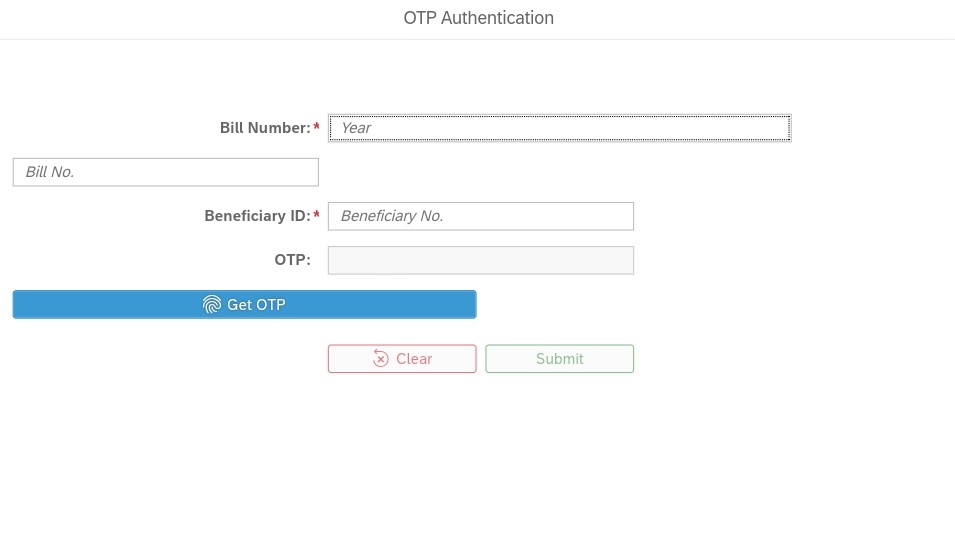
Government Sector CFMS (e.g., Andhra Pradesh CFMS):
1.Identify the Relevant Portal: Different states or government departments in India might have their own CFMS portals. Search online for the specific CFMS you need, such as “https://prdcfms.apcfss.in:44300/”.
2.Locate the Status Inquiry Section: Once on the portal, look for sections labeled “Citizen Services,” “Bill Status,” or “Track Transactions.” The specific wording may vary.
3.Enter Required Information: You’ll likely need to provide some identification details like beneficiary ID, bill number, or challan number (depending on the system).
4.Submit and View Status: Enter the required information and submit the inquiry.The system will display the current status of your bill, payment, or other transaction.
Private Sector “CFMS” (ERP Systems):
1.Access the ERP System: You’ll likely need to log in to a company-specific internal system using your employee credentials.
2.Locate the Reporting or Inquiry Module: The specific module name might vary, but look for sections related to “Financial Reports,” “Transaction Status,” or “Inquiry.”
3.Select the Appropriate Option: Within the module, choose the option relevant to your inquiry.This could be bills payable, expense reports, or specific project budgets.
4.Apply Filters and View Status: Depending on the system, you might be able to filter by date, department, or other criteria to narrow down your search.The system will then display the relevant status information.
Read Also
Additional Tips
• If you’re unsure about the specific CFMS or portal to use, consult the relevant government department or your company’s IT department for guidance.
• Some CFMS might require additional authentication steps like entering a one-time password (OTP) received via SMS.
• The available status details can vary depending on the CFMS. It might show basic information like “pending” or “processed,” or provide more granular details about the transaction stage.
Remember, these are general steps, and the specific process might differ depending on the CFMS implementation you’re using.
FAQ’s
What is a CFMS?
CFMS = Comprehensive Financial Management System. Software for managing an organization’s finances.
Benefits of CFMS?
Saves time, improves accuracy, better decisions, easier collaboration, potentially reduces costs.
How to access a CFMS?
Depends on the system (government or private) and your role (citizen or employee).
Services offered by a CFMS?
Varies – bill payments, applications, budgeting, reporting (depending on type).
Applying for a CFMS?
Usually not needed.Citizen portals might require registration,company access comes through IT.
CFMS,Cfms employee pay details,CFMS Bill Status,CFMS login,CFMS Bill Status 2024,cfms.ap.gov.in citizen bill status,CFMS Challan,cfms bill status 2024,Pay Slip CFMS Bill Status